

Rifampicin is to be added when there is osteomyelitis or other deeper-structure involvement. Clarithromycin and ethambutol combination treatment may be optimally suited in terms of efficacy and tolerability. The recommended approach is to use combination of two active agents until 1–2 months after resolution of lesions or for a minimum of 6 months. Ethambutol, rifampicin, clarithromycin minocycline/doxycycline, ciprofloxacin, and trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole have been used. marinum is resistant to the antituberculosis medications isoniazid, pyrazinamide, and para-aminosalicylic acid and shows intermediate sensitivity to streptomycin. Patients usually do not seek medical attention until their symptoms worsen. marinum invades deeper tissues, such as tendon sheaths, bursae, bones, and joints in up to 29% of cases, irrespective of the patient's immunological state.
Swimmers itch on face pictures skin#
Infections confined to the skin may heal spontaneously over months. Histopathological examination and culture are confirmatory. A sporotrichoid pattern may be seen in up to 20% of cases due to lymphatic spread of the infection. Potential vectors include fish, snails, shellfish, dolphins, and water fleas.Ĭlinical features: Verrucous plaques or nodules occur over the extremities, especially the fingers and bony prominences about 6 weeks after inoculation. Swimming pool granuloma (Syn: Fish tank granuloma, fish fancier's granuloma)Ĭause: Swimming pool granuloma is caused by atypical mycobacteria, including Mycobacterium marinum and Mycobacterium scrofulaceum, residing in both fresh and salt waters – swimming pools, beaches, rivers, lakes, and aquaria. Subsequent exposure results in lesions within hours. The immunogenic enzymes of the cercariae result in sensitization 2 weeks after the first contact.

Humans represent the final hosts as the larvae eventually die within the skin. These miracidiae infect snails and transform into cercaria larvae that penetrate the human stratum corneum using proteolytic enzymes. Birds and rodents, the definitive hosts, excrete schistosome ova into the water that mature into free-swimming miracidiae. Consequently, cercarial dermatitis is now regarded as an emerging disease. Although the first report of cercarial dermatitis was from Mysore, Karnataka, in 1948, the condition has been subsequently reported in hitherto unknown regions such as the Doon Valley of Uttarakhand, with similar trends reported worldwide. Freshwater species of Schistosoma, marine species of Austrobilharzia and Ornithobilharzia, and freshwater/marine species of Trichobilharzia, Gigantobilharzia, Anserobilharzia, Allobilharzia, and Dendritobilharzia have been implicated. Swimmer's itch (Syn: Schistosome dermatitis, cercarial dermatitis, and clam-digger's itch)Ĭause: Cercarial dermatitis is a condition that occurs in both marine and freshwater habitats caused by mammalian and avian schistosomes of family Schistosomatidae. A sizeable section of the population is thus exposed to the aquatic environment and its potential effects. Most major cities of India are located on the banks of rivers that provide livelihood to a large number of people. Eight major rivers and numerous tributaries crisscross about 15,000 km of the Indian landmass. An estimated 4 million fishermen depend on the seas for their livelihood. Its coastal biodiversity encompasses marine algae, seagrasses, mangroves, and aquatic animals including crustaceans, echinoderms, reptiles, pisces, and mammals. India has a long coastline measuring 7516.6 km bordering nine states and four union territories its 73 coastal districts are home to 14.2% of her total population. Since the beginning of time, the aquatic environment has shaped the very character of our planet and has profoundly influenced human civilization. The Aquatic World: Water constitutes two-thirds of the surface area of our planet.
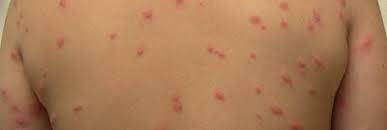
“All is born of water, all is sustained by water” Goethe


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
